Sony identifies 4 errors with CMA's data model, says data is off by at …
A bit ago, the CMA determined that Microsoft has no ability or incentive to foreclose Sony in regards to the Microsoft-Activision merger. Now Sony has delivered a response to the CMA’s findings, calling the agency’s data modelling into question.

![]() 9
9
VIEW GALLERY – 9 IMAGES The CMA recently filed its own Provisionary Findings Addendum that concludes Microsoft has no incentive or ability to foreclose Sony using Call of Duty exclusivity.
This determination is based on what is called an LTV model, or a system that attempts to quantify the lifetime value of a video game player, which was used to estimate how Call of Duty exclusivity would affect both Microsoft and Sony. The model attempts to gauge the implied lost or gained value from consumers switching from PlayStation to Xbox if Call of Duty were to become exclusive. Based on the CMA’s findings, Microsoft has no real motivation to withhold Call of Duty on PlayStation, thus one of the CMA’s theories of harms–the partial or full foreclosure of rivals in the console gaming segment–has been squashed.
Predictably, Sony did not approve of this assessment, and the CMA has published Sony’s response to the new findings. Sony Interactive Entertainment legal counsel has identified four errors with the new PF (Provisionary Findings) report.
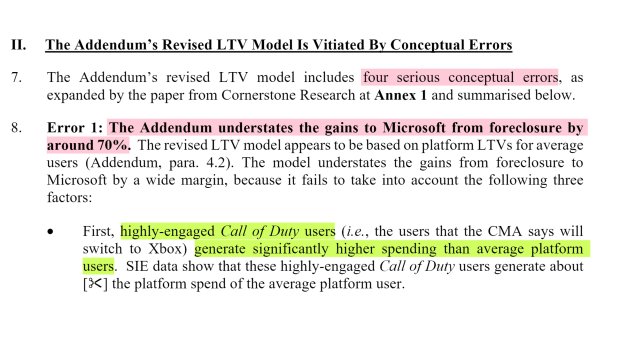
![]() 9
9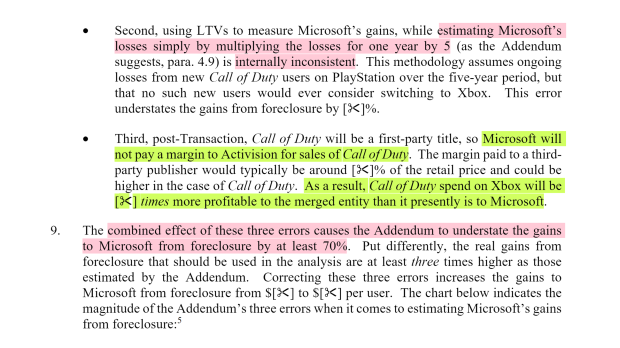
![]() 9
9
First Error
Sony argues that the CMA’s LTV model, or lifetime value model, uses data that was specifically created by Microsoft for use in such a model. Sony says that the model is off by as much as 70% for a number of reasons, including the fact that the CMA’s data model only recognizes average users and not “highly-engaged Call of Duty users”.
Call of Duty players generate “significantly higher spending” than other users on PlayStation platforms, Sony says. Sony also has issues with how the CMA calculated Microsoft’s potential losses from pulling Call of Duty from PlayStation. Counsel further makes the point that Call of Duty will be many times more profitable to Xbox on a post-merger basis because Microsoft will not have to pay a third-party royalty to Activision.

![]() 9
9
Second Error
Here it looks like Sony may be accusing Microsoft of presenting potentially misleading information.
Sony says that the CMA used LTV data that was specifically prepared by Microsoft for such a revised model. However, the original data model used in the CMA’s first-published PF report indicates possible foreclosure incentives. To put it in another way, the first LTV model indicated Microsoft could gain quite a bit from making Call of Duty exclusive, whereas this new model, which includes information and data directly provided by Microsoft, indicates that Microsoft would lose tremendously by pulling Call of Duty from PlayStation.
Sony argues that the original LTV model that led to the foreclosure recognition from the CMA used contemporaneous documents, or documents that were essentially produced in ordinary business activities. The new LTV model, Sony says, “discards this contemporaneous evidence and instead adopts, without apparent explanation, Microsoft’s adjusted LTV estimates that are lower than those in its contemporaneous documents and were created solely for the purposes of this proceeding.” Sony cannot rightly understand how the CMA came to its conclusions based on the data provided.
Nearly all of the data included in the LTV models are redacted so it is very difficult to interpret specific findings.

![]() 9
9
![]() 9
9
Third Error
Sony mentions a very interesting tidbit that hasn’t been talked about very much: The CMA’s LTV model do not reflect the “significant strategic benefits” of bringing Activision games to Game Pass. These benefits were not included in the original LTVs used for the first-published Provisionary Findings, nor are they present or included in the newly-revised Provisionary Findings Addendum. This indicates the LTV model did not reflect one of the biggest parts of the Microsoft-Activision merger.
In its new PF report, which concluded Microsoft had no incentive of partially foreclosing Sony due to the enormous losses it would incur from pulling Call of Duty from PlayStation, the CMA notes that the perceived gains from adding Activision games to Game Pass would not mitigate the losses of removing games from PlayStation entirely. However, Sony argues that this assessment is “not consistent with the CMA’s duty to base its decisions on evidence, rather than speculation.” If potential gains from Game Pass were not quantified in the LTV, then Sony believes the CMA’s assertion in regards to Game Pass to be speculative in nature.

![]() 9
9
![]() 9
9
Fourth Error
The final error is based around how the CMA collected its evidence for the LTV model.
The CMA surveyed UK gamers in an attempt to determine how many people would switch from PlayStation to Xbox. Certain criteria was used to narrow the pool of gamers to those who were more regularly involved with Call of Duty. The data from the pool of surveyed users was narrowed to include those who had spent least £100 and 10 hours on Call of Duty.
These users were more apt to switch from PlayStation to Xbox, the CMA had found. Sony argues that this isn’t correct and that users who play for less than 10 hours shouldn’t be discounted; after all, these users did buy the game. Sony says that 10 hours isn’t a good measurement because it discounts users who buy the game simply to play the singleplayer campaigns; COD campaigns last around 6-8 hours, which is just under the 10-hour threshold.
Sony argues that these players should not be discounted from data.
Sony also confirms that they would have to make a payment in order to accept the 10-year Call of Duty licensing proposal.





